JVM
##[[JVM (Java Virtual Machine)]]
- All applications made with Java is run on JVM
Normal Application : [ Java Application ] + [OS(windows, linux)] + [Computer(Hardware)] Java Application : [ Java Application ] + [ JVM ] + [OS(windows, linux)] + [Computer(Hardware)]
Because Java has JVM,
- write once, run anywhere is possible
- it may be slower than non JVM apps. => JIT compiler
JDK and JRE(Java Runtime Environment)
“JDK” contains
- javac.exe : compiler that compiles Java source code to byte code
- java.exe : interpreter that intereprets and executes byte code produced by the compiler
- javap.exe : reverse assembler that translates class files to java source files
“JRE” is a subset of JDK
- it does NOT have Java compiler or libraries like Javadoc and jdb.
- it can be used just to ‘run’ Java byte code, a compiled version of Java application.
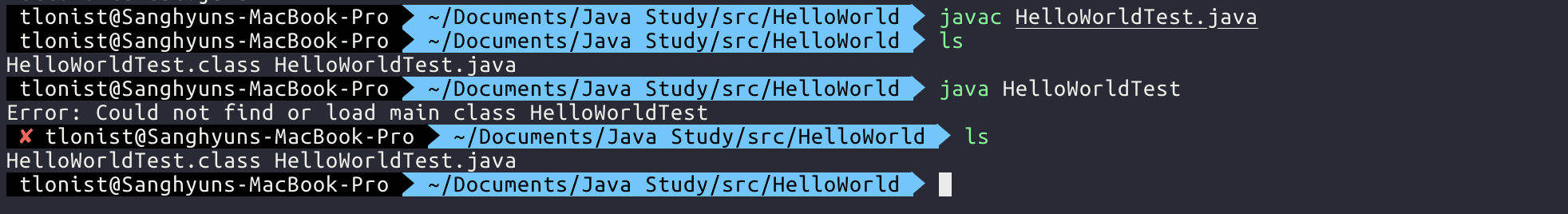
How to run a really simple Java Code?
- Create HelloWorld.java
class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("Hello world!"); } } - Run the class file using Java command. It may seem strange that the above doesn’t work as expected. ‘javac’ must have compiled the .java code into bytecode, and JVM should be able to run the compiled bytecode. Why doesn’t this work?
The answer is very well illustrated in this link. https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18093928/what-does-could-not-find-or-load-main-class-mean