Spring Security - reading official document
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/reference/html5/#servlet-authentication
Prelude
How does spring security work? What do I need to configure and implement? How can I request authentication from my frontend framework? In my team, the security and authentication part of the application was build long before, and all I needed to do was to use them without altering it. Now that I’m trying to build my own web application using Spring Security, I am literally finger-tied by my ignorance. This posting is a trial to understand and be confident on the subject of Spring Security. [https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/reference/html5/#servlet-applications]
What I want to do
- General architecture of Spring Security
- What to do to implement
- set login page
- user authentication (login) with different logic
- allow / disallow specific APIs
- set csrf and cors settings
1. The general architecture of Spring Security
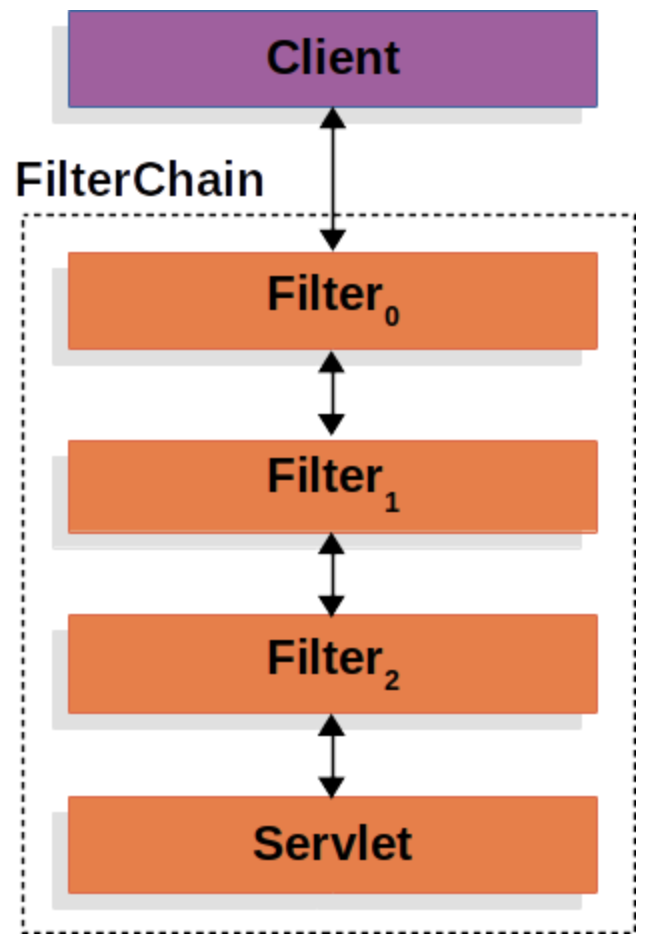
Filter Chain
- This is the most general picture of Spring Security. Basically, it creates various filters for filtering out user requests at various levels.
-
To be more specific, the application creates FilterChain which contains the Filters and Servlet that Processe the HttpServletRequest from clients.
- FilterChain can 1) Prevent lower level Filters or servlets from being invoked 2) Modify request or response to be passed to Filters and servlets
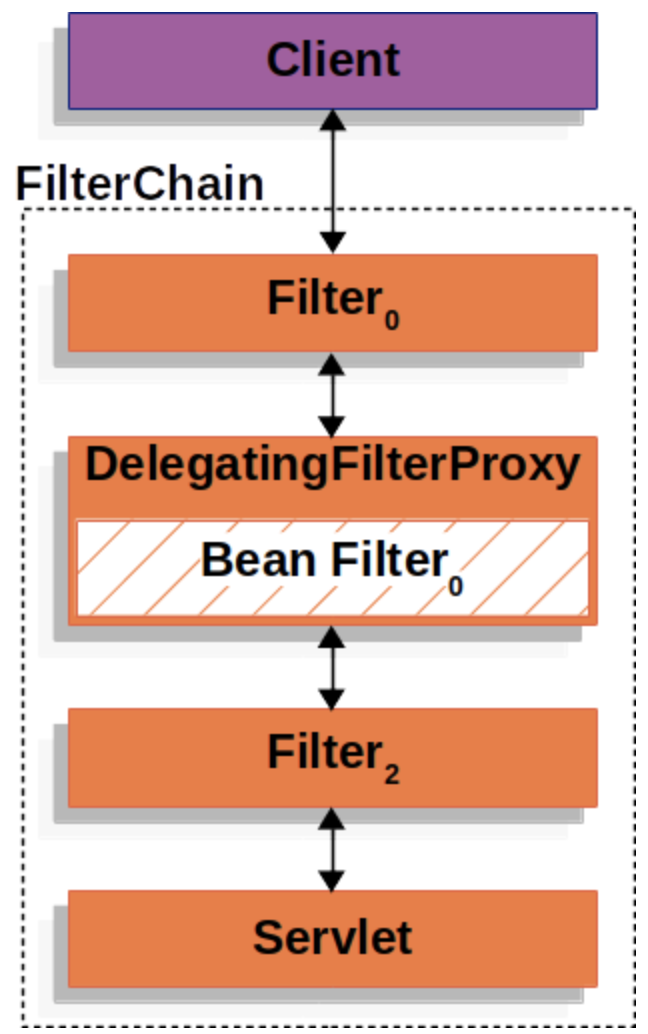
DelegatingFilterProxy
- DelegatingFilterProxy is a Filter Implementation. It can be registered via standard servlet container mechanisms, and delegates all the work to a Spring bean that implements filter.
FilterChain contains many Filters which are delegated by DelegatingFilterProxy.
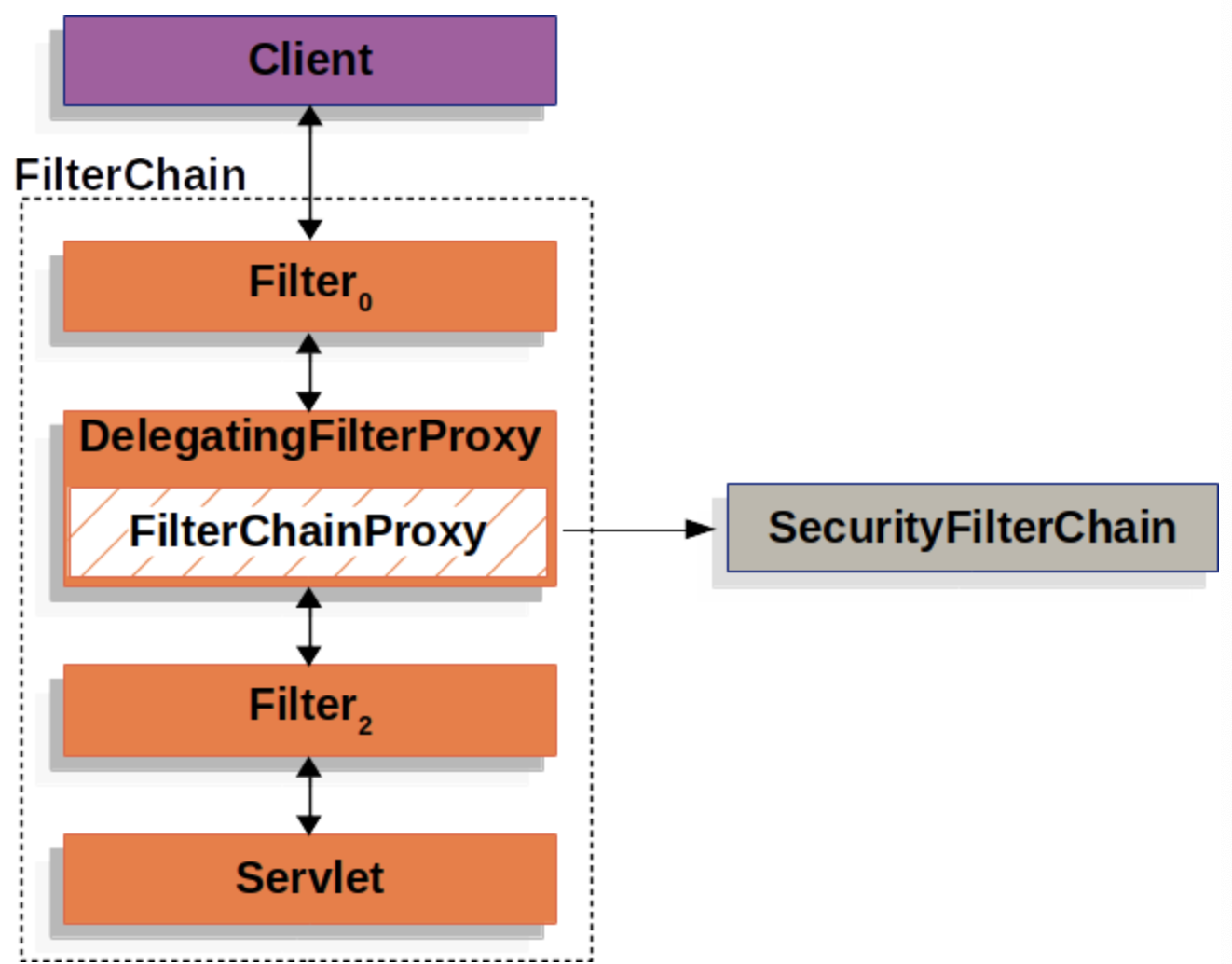
FilterChainProxy
FilterChainProxy is a Filter provided by Spring Security. It allows delegating to other filter instances through SecurityFilterChain. FilterChainProxy is a bean wrapped in DelegatingFilterProxy.
FilterChainProxy inside of DelegatingFilterProxy allows delegation through SecurityFilterChain.
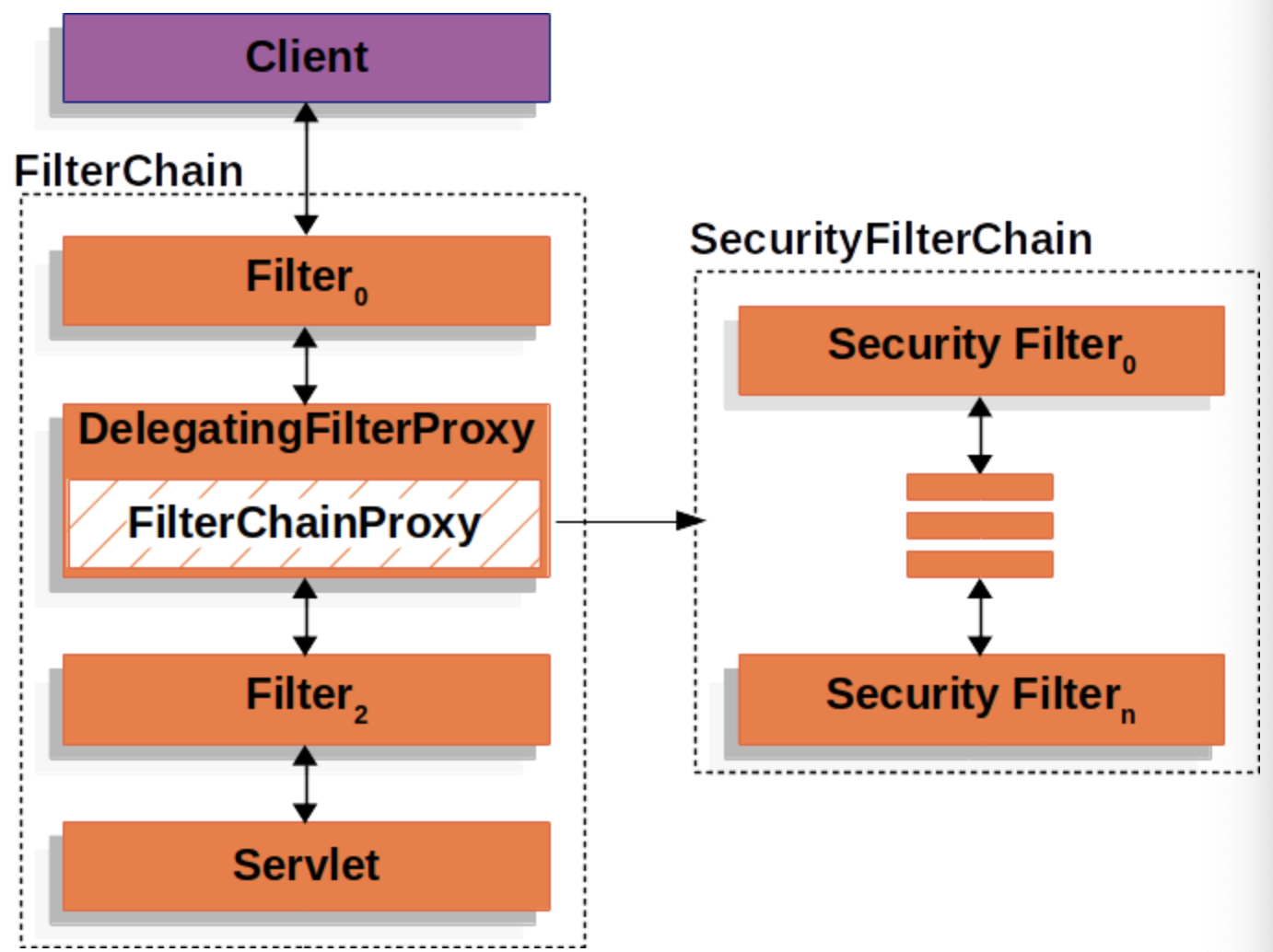
SecurityFilterChain
Security Filters in SecurityFilterChain are beans registered with FilterChainProxy. Each SecurityFilterChains can be uniquely configured. Security Filters are inserted into FilterChainProxy with the SecurityFilterChain API.
To sum up…
- FilterChain creates filters and servlets for filtering.
- DelegatingFilterProxy is a filter implementation that delegates filtering work to filters.
- FilterChainProxy is a bean inside of DelegatingFilterProxy that uses SecurityFilterChains to perform filtering by delegating works to filters.
- SecurityFilterChains can be uniquely configured.
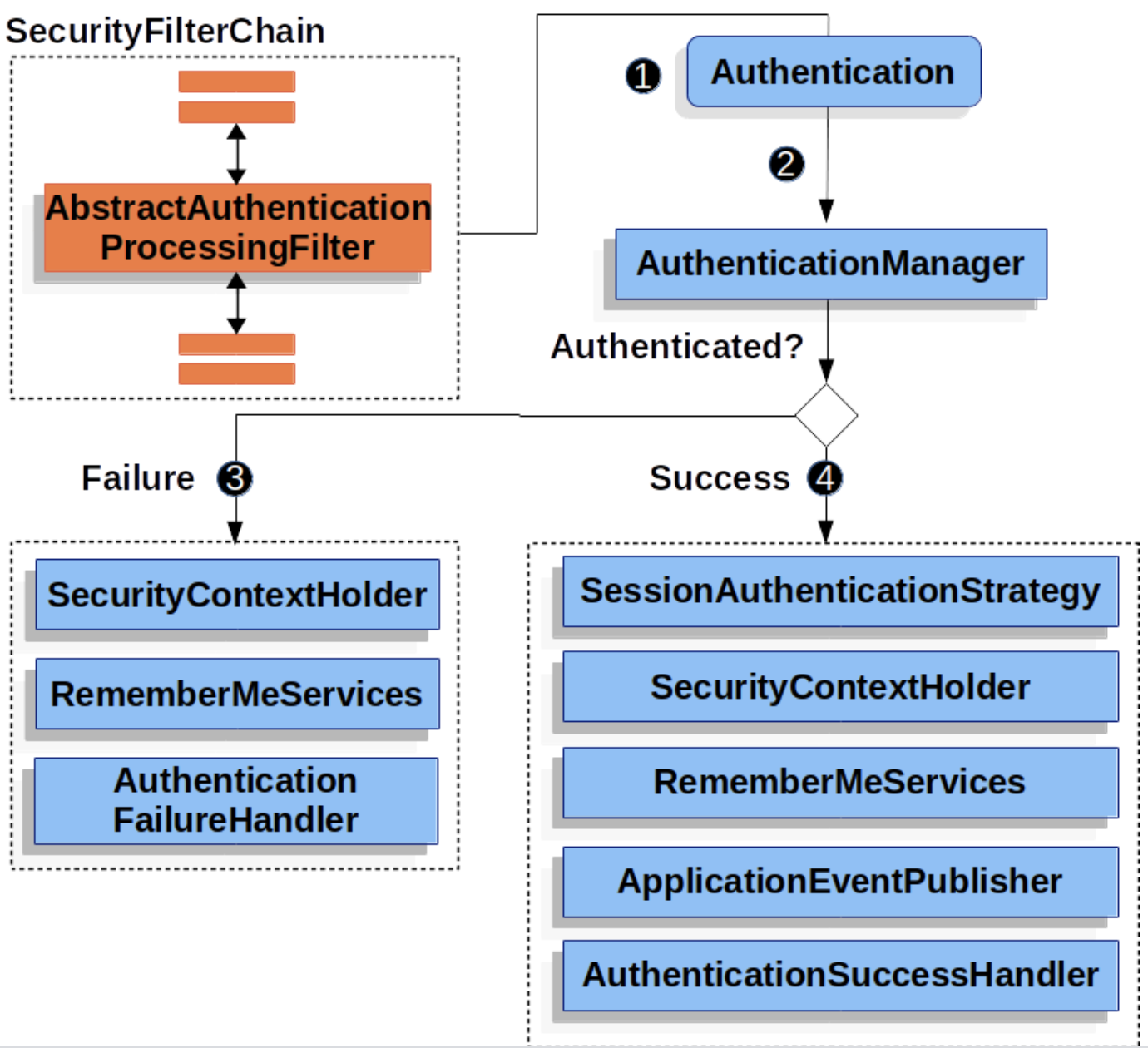
2. Authentication
SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder is where Spring Security holds the details of who is authenticated. Below is the sample code.
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
Authentication authentication =
new TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER");
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);
You can access to a currently authenticated user like below.
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
String username = authentication.getName();
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();
SecurityContext
- SecurityContext is obtained from the SecurityContextHolder; it contains an Authentication object.
Authentication
- Authentication is an input to AuthenticationManager to provide credentials a user has provided to authenticate.
- It contains
- principal : As an instance of UserDetails, it identifies the user.
- credentials : Often a password. It gets cleared after a user is authenticated to prevent leakage.
- authorities : The level of permissions a user is granted.
GrantedAuthority
- GrantedAuthorities can be obtained from the Authentication.getAuthorities() method. This provides a Collection of GrantedAuthority objects - which are roles such as ROLE_ADMIN or ROLE_USER. These roles are later configured for web, method and domain object authorization.
AuthenticationManager
- AuthenticationManager is the API that defines how Spring Security’s Filters perform authentication. The most common implementation is ProviderManager.
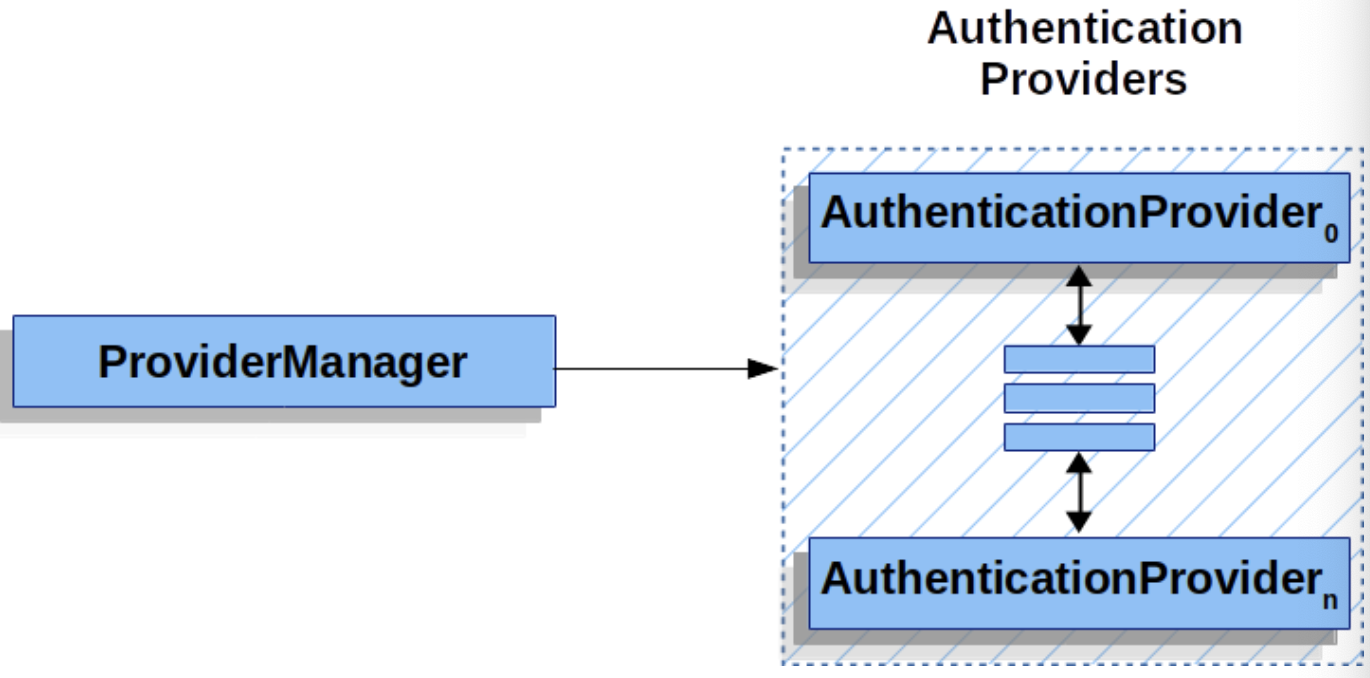
ProviderManager
- ProviderManager delegates to a list of AuthenticationProviders the job of authenticating a user. In practice each AuthenticationProvider knows how to perform a specific type of authentication. For example, one AuthenticationProvider might be able to validate a username/password, while another might be able to authenticate a SAML assertion.
AuthenticationEntryPoint
Topics regarding Login In Practice/ Allowing Access to Specific URLs/ CORS and CSRF issues will be covered subsequently.